Russia has been accused of planning to use thermobaric weapons - also known as vacuum bombs - in its invasion of Ukraine. These are controversial because they are much more devastating than conventional explosives of similar size, and have a terrible impact on anyone caught in their blast radius.
How does a vacuum bomb work?
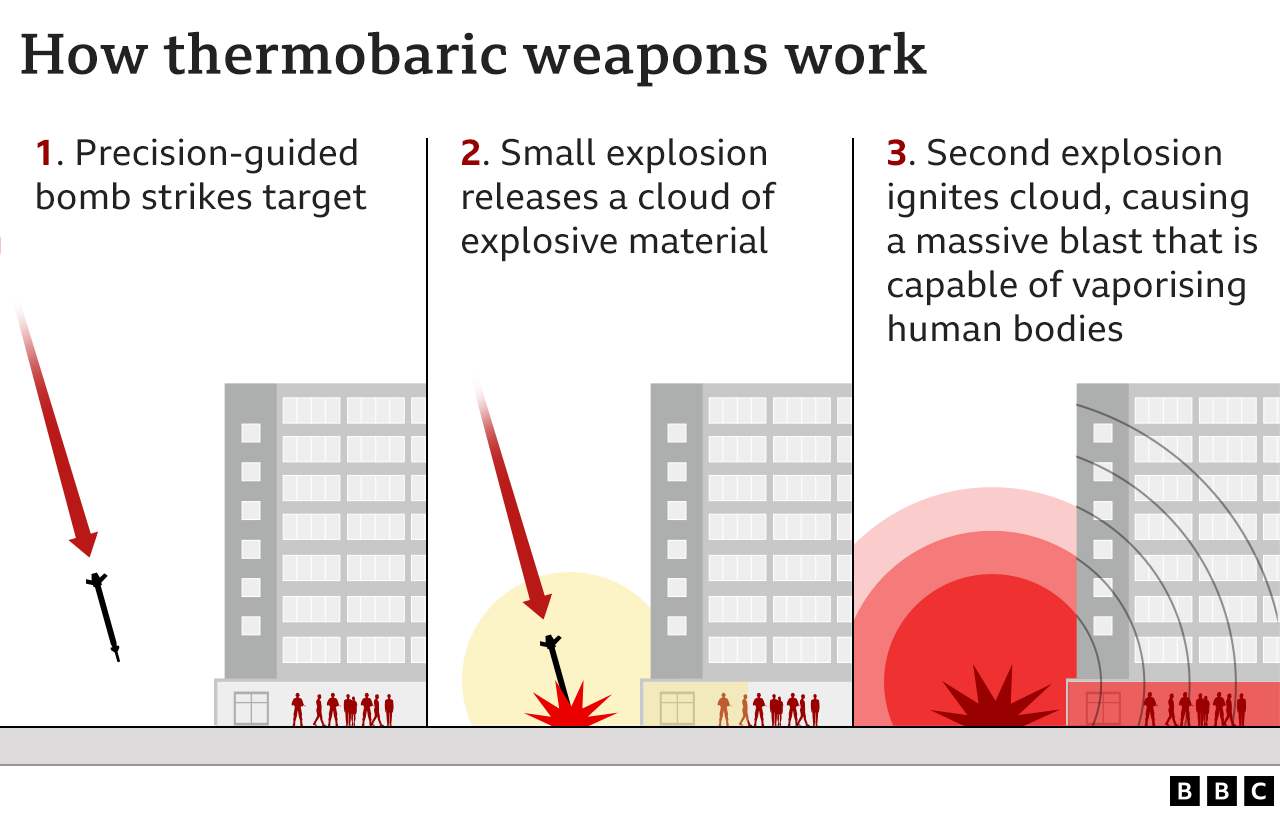
A vacuum bomb, also called an aerosol bomb or fuel air explosive, consists of a fuel container with two separate explosive charges. This can be launched as a rocket or dropped as a bomb from aircraft. When it hits its target, the first explosive charge opens the container and widely scatters fuel mixture as a cloud.
This cloud can penetrate any building openings or defences that are not totally sealed. A second charge then detonates the cloud, resulting in a huge fireball, a massive blast wave and a vacuum which sucks up all surrounding oxygen. The weapon can destroy reinforced buildings, equipment and kill or injure people.
They are used for a variety of purposes and come in a range of sizes - including weapons for use by individual soldiers such as grenades and hand-held rocket launchers. Huge air-launched versions have also been designed, specifically to kill defenders in caves and tunnel complexes - the effects of this weapon are at their most severe in enclosed spaces.
In 2003, the US tested a 9,800kg bomb, nicknamed the "Mother of all bombs". Four years later, Russia developed a similar device, the Father of all bombs". This created an explosion equivalent to a 44-tonne conventional bomb - making it the biggest non-nuclear explosive device in the world. READ MORE...

No comments:
Post a Comment