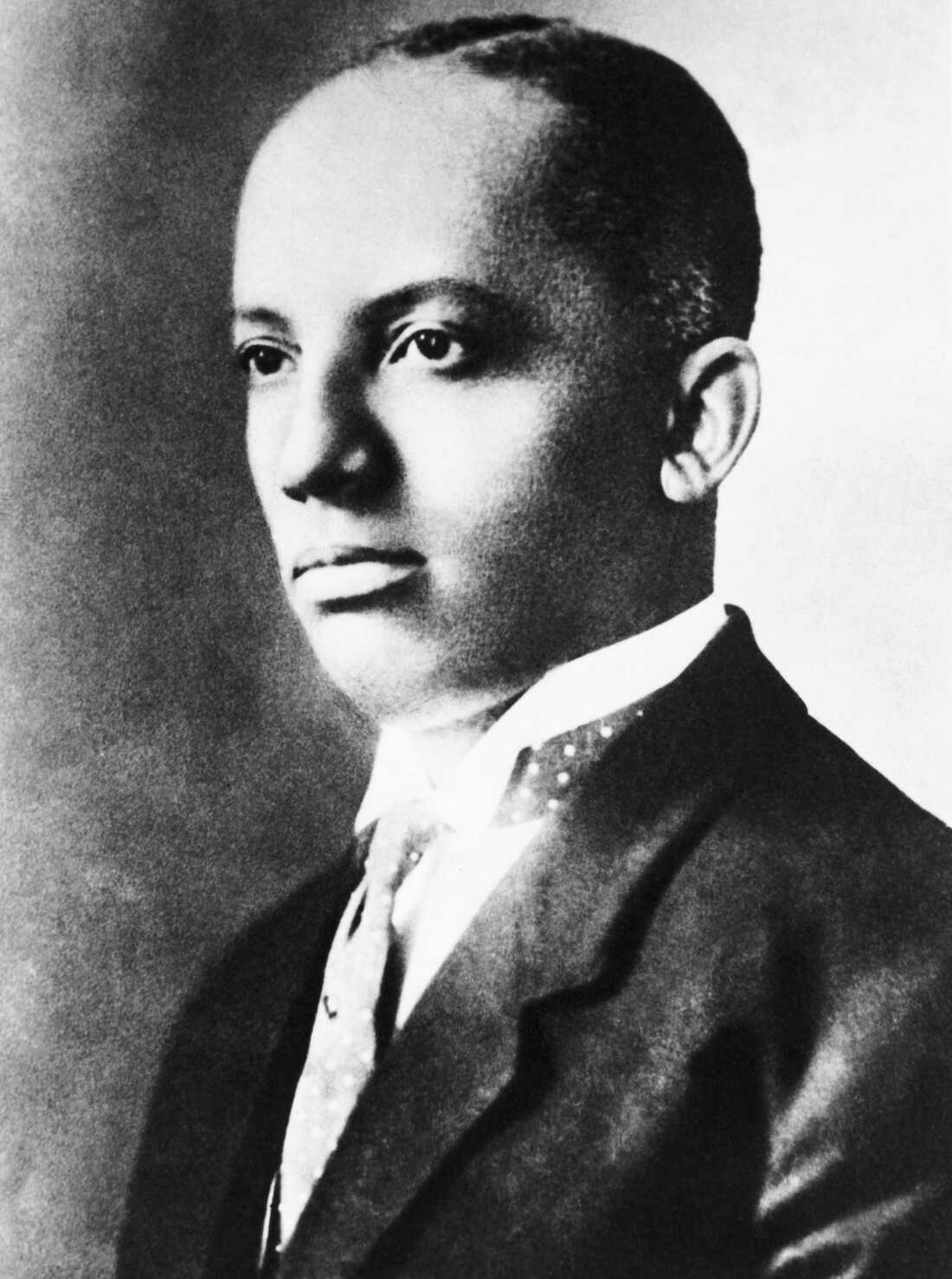
Carter G. Woodson (1875-1950) was an American historian, a scholar and the founder of the Association for the Study of Negro Life and History. Woodson was instrumental in launching Negro History Week in 1926.Bettmann Archive/Getty Images
Every February, the U.S. honors the contributions and sacrifices of African Americans who have helped shape the nation. Black History Month celebrates the rich cultural heritage, triumphs and adversities that are an indelible part of our country's history.
This year's theme, Black Health and Wellness, pays homage to medical scholars and health care providers. The theme is especially timely as we enter the third year of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has disproportionately affected minority communities and placed unique burdens on Black health care professionals.
"There is no American history without African American history," said Sara Clarke Kaplan, executive director of the Antiracist Research & Policy Center at American University in Washington, D.C. The Black experience, she said, is embedded in "everything we think of as 'American history.' "
First, there was Negro History Week. Critics have long argued that Black history should be taught and celebrated year-round, not just during one month each year.
It was Carter G. Woodson, the "father of Black history," who first set out in 1926 to designate a time to promote and educate people about Black history and culture, according to W. Marvin Dulaney. He is a historian and the president of the Association for the Study of African American Life and History (ASALH).
Woodson envisioned a weeklong celebration to encourage the coordinated teaching of Black history in public schools. He designated the second week of February as Negro History Week and galvanized fellow historians through the Association for the Study of Negro Life and History, which he founded in 1915. (ASNLH later became ASALH.)
The idea wasn't to place limitations but really to focus and broaden the nation's consciousness. "Woodson's goal from the very beginning was to make the celebration of Black history in the field of history a 'serious area of study,' " said Albert Broussard, a professor of Afro-American history at Texas A&M University.
The idea eventually grew in acceptance, and by the late 1960s, Negro History Week had evolved into what is now known as Black History Month. Protests around racial injustice, inequality and anti-imperialism that were occurring in many parts of the U.S. were pivotal to the change. READ MORE...
This year's theme, Black Health and Wellness, pays homage to medical scholars and health care providers. The theme is especially timely as we enter the third year of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has disproportionately affected minority communities and placed unique burdens on Black health care professionals.
"There is no American history without African American history," said Sara Clarke Kaplan, executive director of the Antiracist Research & Policy Center at American University in Washington, D.C. The Black experience, she said, is embedded in "everything we think of as 'American history.' "
First, there was Negro History Week. Critics have long argued that Black history should be taught and celebrated year-round, not just during one month each year.
It was Carter G. Woodson, the "father of Black history," who first set out in 1926 to designate a time to promote and educate people about Black history and culture, according to W. Marvin Dulaney. He is a historian and the president of the Association for the Study of African American Life and History (ASALH).
Woodson envisioned a weeklong celebration to encourage the coordinated teaching of Black history in public schools. He designated the second week of February as Negro History Week and galvanized fellow historians through the Association for the Study of Negro Life and History, which he founded in 1915. (ASNLH later became ASALH.)
The idea wasn't to place limitations but really to focus and broaden the nation's consciousness. "Woodson's goal from the very beginning was to make the celebration of Black history in the field of history a 'serious area of study,' " said Albert Broussard, a professor of Afro-American history at Texas A&M University.
The idea eventually grew in acceptance, and by the late 1960s, Negro History Week had evolved into what is now known as Black History Month. Protests around racial injustice, inequality and anti-imperialism that were occurring in many parts of the U.S. were pivotal to the change. READ MORE...
