A very rare treat is about to grace Earth's night skies.
On the evening of 28 February 2025, all seven of the other planets in the Solar System will appear in the night sky at the same time, with Saturn, Mercury, Neptune, Venus, Uranus, Jupiter, and Mars all lining up in a neat row – a magnificent sky feast for the eyes known as a great planetary alignment.
But that's not all. Between now and then, on 21 January 2025, six of the seven other planets will appear in the sky at once in a large alignment – Mars, Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune, Venus, and Saturn, with the exception of Mercury.
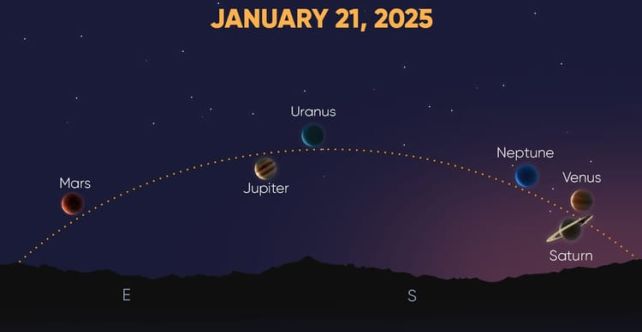
An illustration of the upcoming January planetary alignment as seen from the Northern Hemisphere. (Star Walk)
Actually, it's not uncommon for a few planets to be on the same side of the Sun at the same time, but it's less common for most, or even all of the planets to align.
Any number of planets from three to eight constitutes an alignment. Five or six planets assembling is known as a large alignment, with five-planet alignments significantly more frequent than six.
Seven-planet great alignments are, of course, the rarest of all. READ MORE...
Any number of planets from three to eight constitutes an alignment. Five or six planets assembling is known as a large alignment, with five-planet alignments significantly more frequent than six.
Seven-planet great alignments are, of course, the rarest of all. READ MORE...


